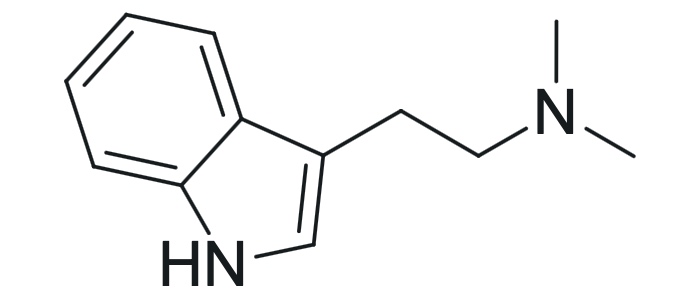
Ayahuasca
Ayahuasca is an orally administered mixture of a DMT-containing plant (usually Psychiotria Viridis/Chakruna, but also Diplopteris Cabrerana/Yage or Mimosa Hostilis/Jurema) and Banisteriopsis Caapi, an MAO inhibitor that is supposed to slow down the metabolism of DMT. The raw materials are legal in Germany, but any processing is prohibited, including ayahuasca.
Ayahuasca originates from the Amazon region and is the most common mind-expanding substance there and in Brazil, although it is only used in a ritual context. It is regarded as feminine and is often referred to as the grandmother. In Peru, it is part of the national cultural heritage.
Ayahuasca can trigger strong hallucinations, but is also suitable for therapeutic use. Its special features are that it has a strong healing effect on the body and its neuroplastogenic effect stimulates nerve growth and the formation of new nerve connections, and that it tastes very unpleasant and often leads to nausea and vomiting. The duration of effect is around 3 hours, but in a traditional context, several doses are given so that the total duration of a session can be expanded.
Ayahuasca should not be confused with 5-MeO-DMT, which also contains DMT and only works for around 50 minutes.
In Switzerland, attempts are being made to replace ayahuasca with synthetic DMT.